Term 1 Second Entry: A Bunsen Burner
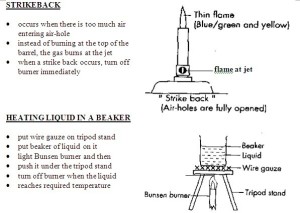
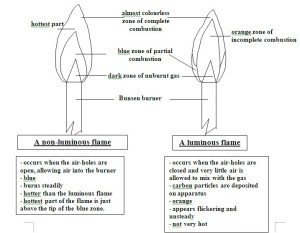
A bunsen burner is an apparatus that ignites fire for the experiments in the Science lab. A bunsen burner, as shown in Figure A, can produce a non- luminous and a luminous flame. A luminous flame is the flame that isn’t really hot. It is flickering, orange/yellow in colour, and can be seen from afar. However, a non- luminous flame is steady, blue in colour and cammot be seen from afar. We use a non- luminous flame for experiments as not only is it hotter than a luminous flame, there is sufficient gas for the fire to burn completely. A bunsen burner is made up of a barrel, a collar, an air-hole, a jet, a base, and a gas tap. Shown in Figure B
Barrel: To raise the flame to a suitable height
Collar: Control the air flowing into the Bunsen Burner
Air-hole: To allow air to enter the Bunsen Burner
Jet: To enable gas to rush out of the gas supply and to draw in air
Base; To support the Bunsen Burner so that it would not topple
Gas Tap: To control the flow of gas to the Bunsen Burner
Now knowing the various parts of the Bunsen Burner, how do we light one?
- Close the air- hole
- Put a gas lighter above the barrel
- Turn on the gas tap
- Strike the lighter to ignite the gas
Open the air- holes until a n0n-luminous flame is obtained.
What is a strike-back? A strike- back will occur when there is too much air holes. We must turn off the gas tap immediately before the flame gets too big and hurt us.